Diagnostic Cardiac Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Assesses the electrical activity of the heart via 12 leads placed on the chest and the limbs. An ECG is used to measure the rate and regularity of heartbeats. It is essential for the diagnosis of a heart attack.
ECGs are also a useful tool in assessing the long term effect of high blood pressure on the heart and in diagnosing a number of other cardiac conditions. There is no preparation necessary for an ECG.
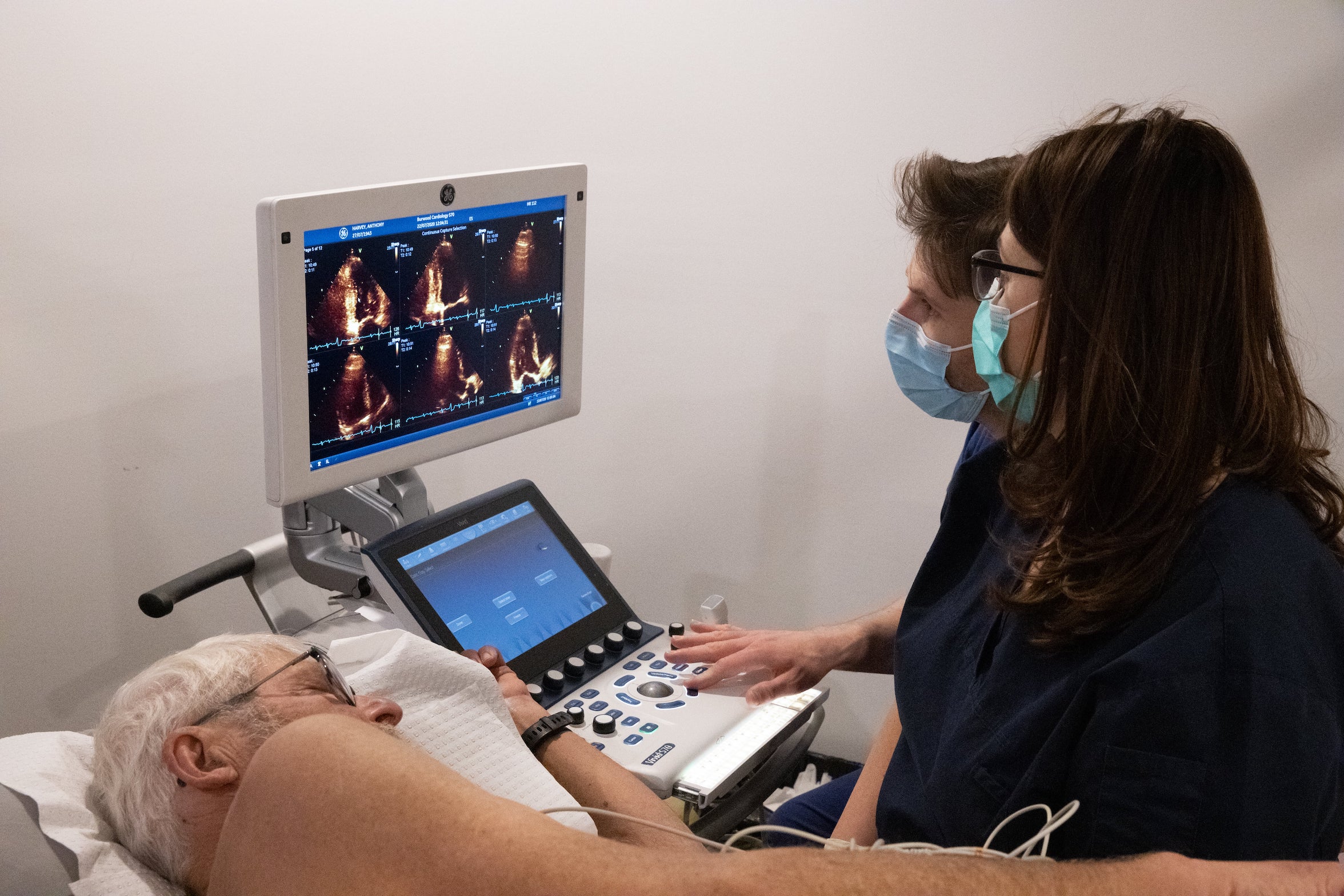
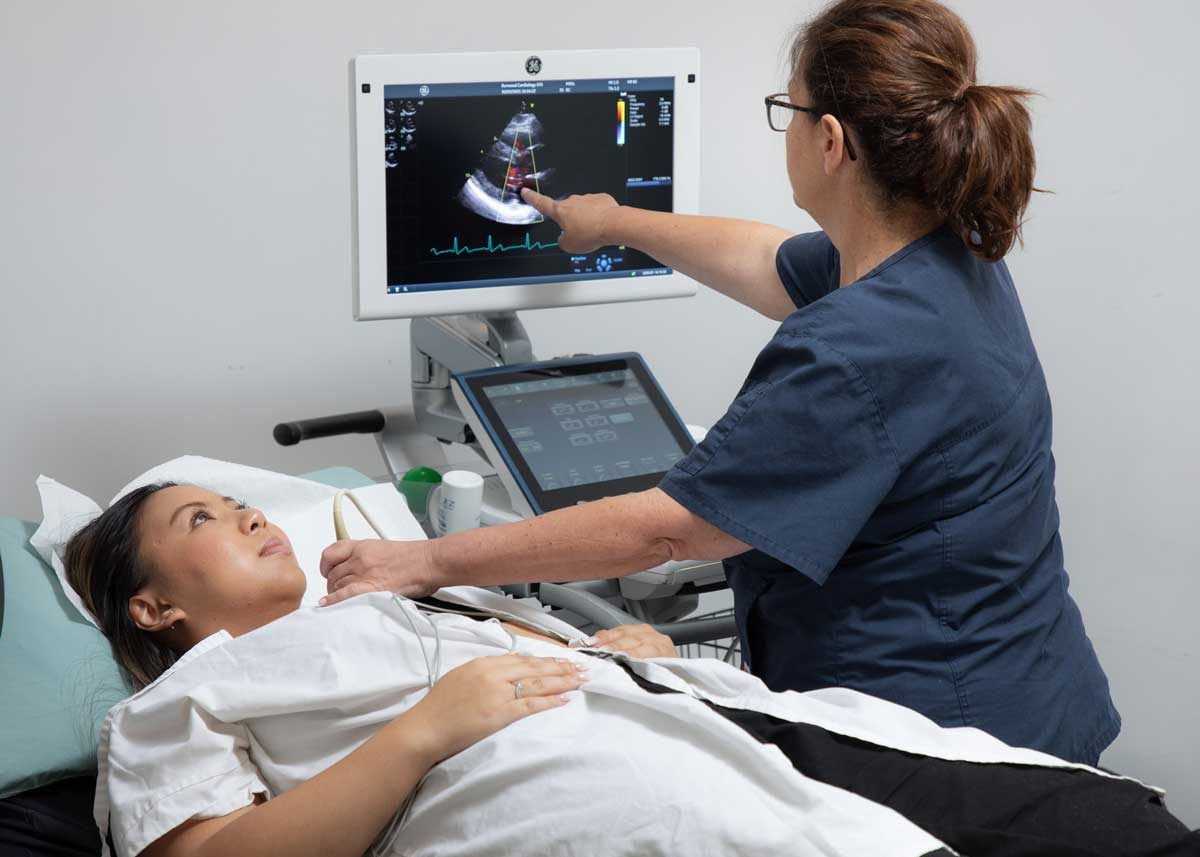
Echocardiogram
Also known as a cardiac ultrasound or 2Dimensional Echo Doppler, this is an imaging test in which high frequency sound waves are used to create a moving picture of your heart to detect structure and function of the heart, measuring the direction and velocity of blood flow.
Echocardiograms give important information about the structure and function of the heart and valves. There is no preparation required for an echocardiogram.
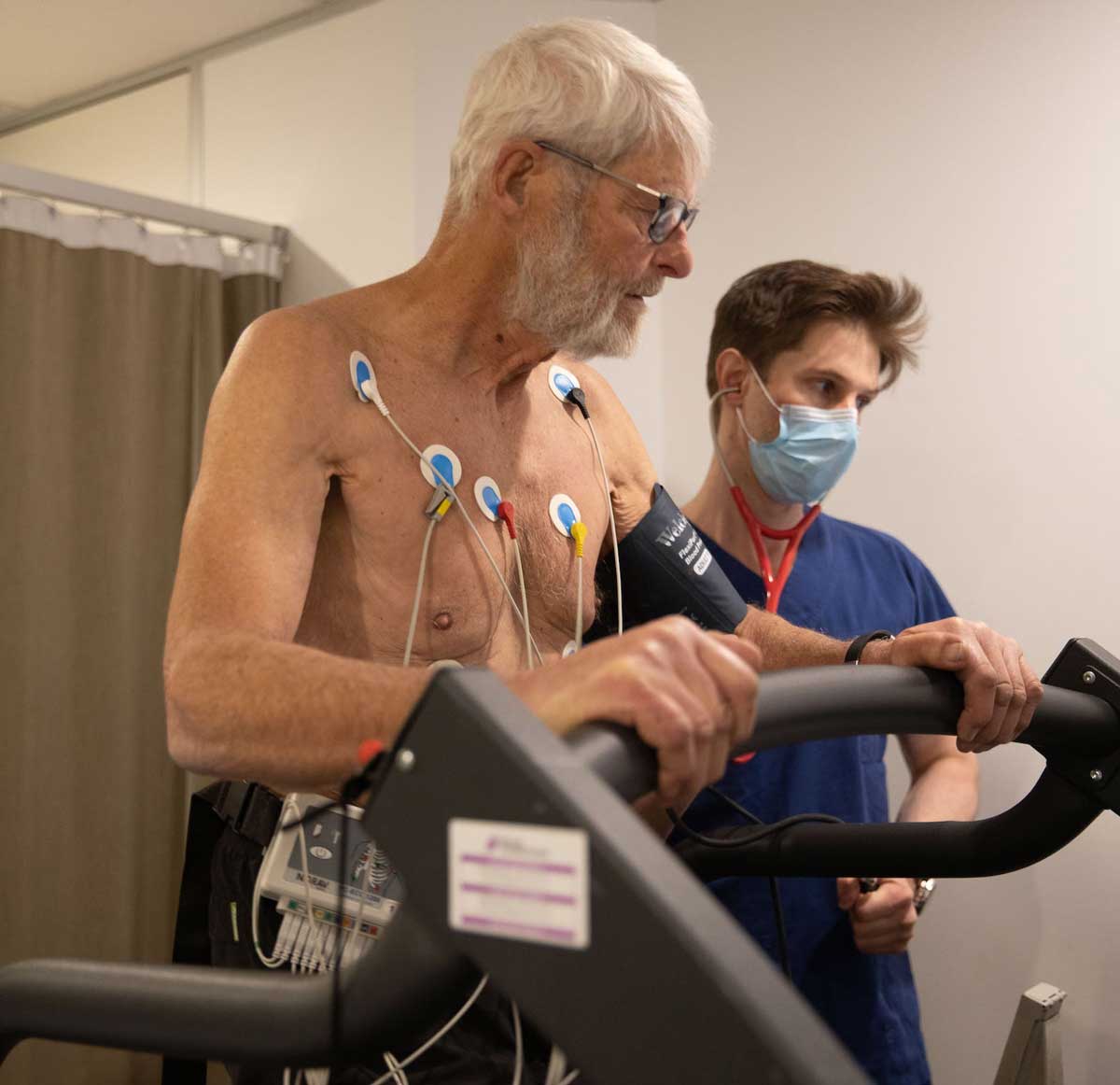
Exercise Stress Testing
An exercise stress test measures a heart’s ability to respond to physical stress-exercise in a controlled clinical environment where the heart is stressed by exercise on a treadmill. This test is used to assess chest pain and effort tolerance and diagnose significant coronary artery disease. The test also assesses your fitness and may also assist in the investigation of abnormal heart rhythms.
Preparation done at the time of the test includes possible shaving of chest hair and then the application of 10 electrodes to the chest and upper abdomen. After baseline data has been captured and entered, exercise commences on a medical grade treadmill using standard protocols. Generally, the speed and incline of the treadmill increases every 3 minutes. Your cardiologist will inform you how long you should aim to walk for. The test is terminated when standard endpoints, including patient requests, are reached. For those less fit or less active there is an option of using a more gentle protocol. Comfortable shoes and walking pants are necessary. Men usually perform this test bare chested and woman in a gown with bra on. There is a small risk associated with this test so consent to proceed is required. A stress test is generally safer than exercising on your own in a gym. An exercise stress test usually takes 30 minutes.
Exercise Stress Echocardiogram
A stress echocardiogram is similar to a standard exercise stress test but provides far more information as both ECG data and echo images are analysed. Cine loops of the heart are captured prior to exercise with a cardiac ultrasound machine using standard protocols.
The monitoring and exercise protocols are the same as for a standard exercise test, however immediately after exercise usually within a matter of seconds, more images are captured. These are then compared side by side with the pre exercise images. Changes in the heart’s shape and function allow for diagnosis of underlying ischaemic heart disease. Stress echocardiography is also useful for the diagnosis and management of other cardiac conditions that require functional imaging under stress (exercise) conditions. The risks and preparation are the same as for a standard exercise test, however a stress echocardiogram will often take a little longer, allow 45 minutes.
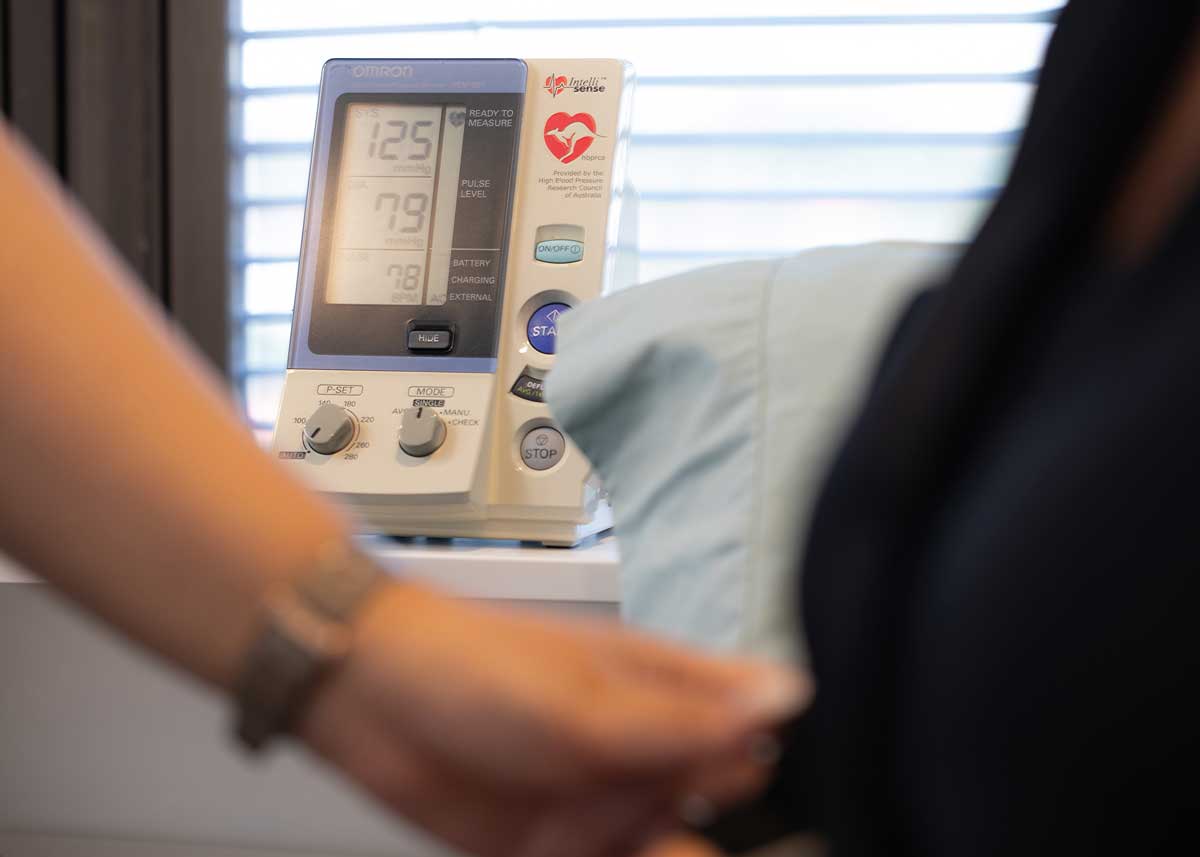
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitor
This is a mobile device the size of a smart phone, attached blood pressure cuff that is placed on the non-dominant arm. This device is programmed to inflate the cuff every 30 minutes during the day and every hour at night in order to measure out of office blood pressure.
An ambulatory blood pressure monitor is useful in diagnosing white coat as well as masked hypertension and assessing adequacy of blood pressure control on treatment. As ambulatory blood pressure monitors are electronic devices they need to be kept dry ie no bathing or showering with one of these monitors on.

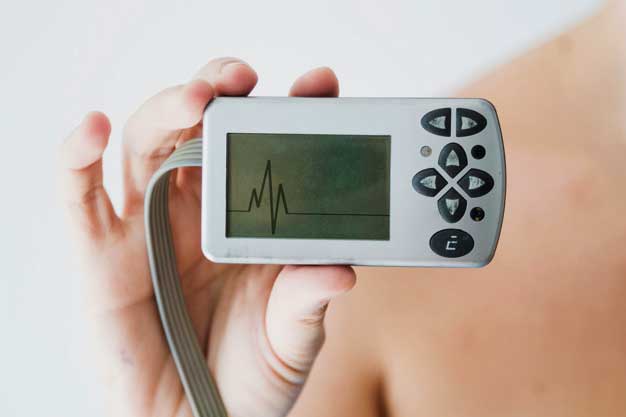
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor is a small, wearable device that keeps track of your heart rhythm. Your doctor may want you to wear a Holter monitor for one to two days. During that time, the device records all of your heartbeats. A Holter monitor test is usually performed after a traditional test to check your heart rhythm (electrocardiogram).
Your doctor uses information captured on the Holter monitor to figure out if you have a heart rhythm problem. If standard Holter monitoring doesn’t capture your irregular heartbeat, your doctor may suggest a wireless Holter monitor, which can work for weeks.
Some personal devices, such as smart watches, offer electrocardiogram monitoring. Ask your doctor if this is an option for you.